Which Best Describes Partial Pressure in a Mixture of Gases
If the partial pressure of the diatomic gas. The partial pressure is the pressure exerted by just one gas inthe mixture.
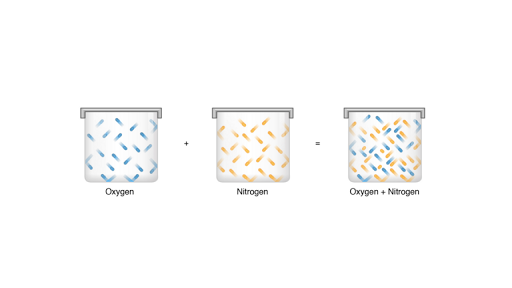
Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure Article Khan Academy
The partial pressure of a gas in solution is.

. What is the partial pressure of a gas in a mixture of gases. Question 1u 3 points Two mixtures of gases are separated by a semipermeable membrane. Describe the movement of molecules between the two mixtures.
The total pressure of a sample is 135 atm and the partial pressure of N2 in the sample is 0742 atm. A representative sample of the liquid and gas are shown in the particulate views. If the total pressure of the gas sample is.
The pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas. Which best defines partial pressure in a mixture of gases. If the partial pressure of hydrogen in the mixture is 75 torr what is the total pressure of the mixture.
Which of the following best describes Charless Law. The chemist heats the mixture and collects some of the first gas produced. Pressure Total Pressure Gas 1 Pressure Gas 2 Pressure Gas 3.
What is the mole fraction of N2 in the sample. The pressure exerted by a particular component of a mixture of gas. Since every gas has an independent behavior the ideal gas law is used to find.
An alternative of this equation can be used to determine the partial pressure of an individual gas in the mixture. A mixture of gases contains 425 grams of CO2 and 225 grams of CH4 and has a total pressure of 0900 atm. The partial pressure of an individual gas is equal to the total pressure multiplied by the mole fraction of that gas.
P N 2 P O 2 P Ar P total. And thus the partial pressure of any component gas is proportional to the mole fraction the constant of proportionality RTV. Calculate the apparent molar mass the apparent gas constant the constant-volume specific heat and the specific heat ratio at 300 K for the mixture.
Definition of molar volume - What is it Meaning and Concept. Which best defines partial pressure in a mixture of gases. Describe its bonding and geometry using a valence bond approach.
Where P 1 P 2 P 3 are the partial pressures of gas 1 gas 2 and gas 3. Since the gas molecules in an ideal gas behave independently of other gases in the mixture the partial pressure of hydrogen is the same pressure as if there were no other gases in the container. The ratio of the number of moles of one component in a mixture to the total number of moles in the mixture.
Gas pressure and gas percentages Added Together equals partial pressure of nitrogen or oxygen pO2. Half of the pressure that is exerted by the gases of a mixture on the container. In an ideal gas mixture the partial pressures of the component gases are as follows.
And N 2 50 kPa. Which of the following takes place in the combustion What is the partial pressure of argon PAr in the flask. Essure that is exerted by one gas as if it occupied a container by itself.
OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR. In a mixture of hydrogen and helium gases the mole fraction of helium is 0750. Boyles Law and the Ideal Gas Law tell us the total pressure of a mixture depends solely on the number of moles of gas and not the kinds of molecules.
Pressure that is exerted by all the gases of a mixture on the container pressure that is exerted by one gas as if it occupied a container by itself half of the pressure that is exerted by the gases of a mixture on the container sum of the individual pressures that are everted by two or more gases. 10atm the partial pressure of H 2 Og in the gas sample produced is predicted to be closest to which of the following. CO 2 125 kPa.
According to Daltons law of partial pressures the total pressure exerted by the mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressure of every existing individual gas and every gas is assumed to be an Ideal gas. THIS USER ASKED. The total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases.
The sum of the partial pressures is equal to the total pressure. If the partial pressure of the diatomic gas is 0510 atm If the partial pressure of the diatomic gas is 0510 atm 22. Mixture B contains oxygen gas partial pressure 1 atm and nitrogen gas partial pressure 1 atm.
O 2 375 kPa. The partial pressure of each gas is just the total pressure multiplied by the mole fraction equal to moles of gas divided by total moles of that gas. Some conclusions you may draw from these results are true for all partial pressure problems.
Mixture A contains oxygen gas partial pressure 75 atm and nitrogen gas partial pressure75 atm. The contribution of hydrogen gas to the total pressure is its partial pressure. And thus now we breathe dioxygen gas at a pressure of approx.
Sum of the individual pressures that are exerted by two or more gases. P total P 1 P 2 P 3. Determine the mole fractions and mass fractions of each component.
Clearly this law assumes a mixture of non-reacting gases. Daltons Law allows us to calculate the total pressure in a system from each gas individual contribution. Pressure that is exerted by all the gases of a mixture on the container.

Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
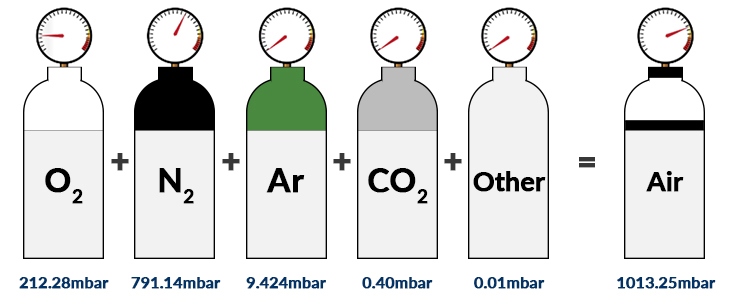
What Is Partial Pressure Of Oxygen And How Do You Calculate It


No comments for "Which Best Describes Partial Pressure in a Mixture of Gases"
Post a Comment